Periodontal Diseases
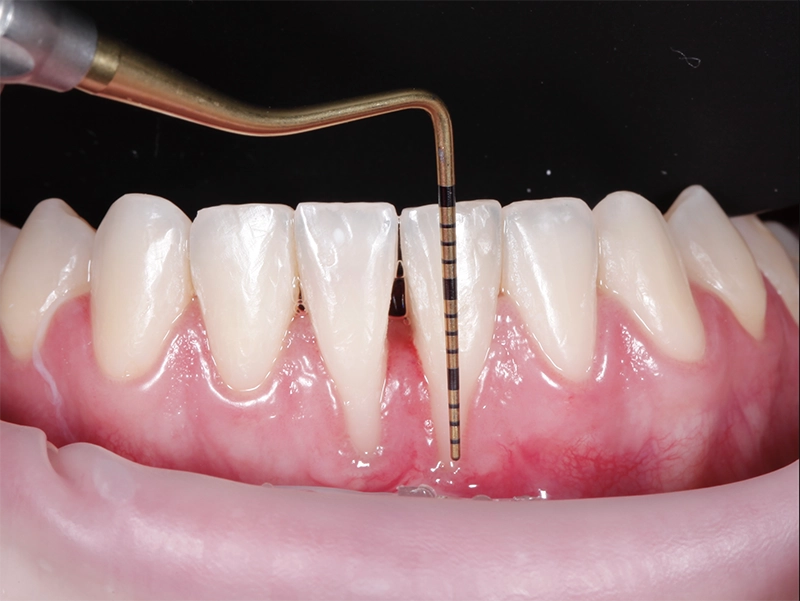
Periodontal diseases, also known as gum diseases, are inflammatory conditions that affect the gums and supporting structures around the teeth. These diseases range from mild gum inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe forms such as periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the earliest and most common form of periodontal disease. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, irritates the gums. Symptoms of gingivitis include redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, especially during brushing or flossing. However, at this stage, the underlying bone and connective tissues are still intact, and the damage is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis. Periodontitis is characterized by the inflammation and infection of the gums, along with damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth. In addition to the symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis may involve gum recession, formation of pockets between the gums and teeth, persistent bad breath, loose teeth, and changes in the bite.
Periodontal diseases are primarily caused by the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. However, other factors like smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, genetic predisposition, and systemic conditions such as diabetes can increase the risk and severity of periodontal diseases.
Effective treatment for periodontal diseases depends on the stage and severity of the condition. In the early stages of gingivitis, professional dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and antimicrobial mouth rinses, can help reverse the inflammation and prevent further progression.


For more advanced cases of periodontitis, treatment may involve scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. In some cases, surgical interventions like flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue regeneration may be necessary to restore the health and structure of the affected tissues.
Prevention and ongoing maintenance are essential in managing periodontal diseases. This includes practicing good oral hygiene, attending regular dental check-ups and cleanings, and adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and avoidance of tobacco products.
Periodontal diseases are a significant oral health concern as they can lead to tooth loss and have been linked to systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems. Early detection, prompt treatment, and consistent oral care are crucial in preventing the progression of periodontal diseases and maintaining optimal oral health. It is important to consult with a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and guidance on maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
Improving your dental and overall health!

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Quick Links
- Home
- Dr Manol Ivchev
- Services
- About Us
- Functional Dentistry
- Blog
- Contacts
Services
- TMJ Disorder Treatment
- Orthodontics
- General Dentistry
- Implantology
- Oral Surgery
- Pediatric Dentistry
Contact Info
- +359 999 999 999
- office@coldydent.com
- Sofia, ul. "Bulgarska Legia" №2